What Exactly is Public Cloud?
Public cloud is one of the most well-known cloud computing models that is being used by consumers today. In a public cloud, all types of cloud services are enabled within a virtualized environment. The applications and storage are provided to the consumer and services are usually charged on a pay-per-consume basis as offered by the public cloud service provider.

Private and Hybrid Clouds
-
Private Cloud
When an organization opts for a private cloud, they derive a full control of the IT infrastructure that is always maintained over a private network. Here, the hardware, as well as software, is solely meant and dedicated to an individual’s business. Private cloud deploys various computing resources exclusively for a single organization and this can be flexible as well as customizable as per the client’s requirements. At times, a private cloud is also known as an enterprise cloud.
-
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is often termed as the “best of the worlds”, i.e. comprising some features like an on-premise infrastructure similar to a private cloud and some features of a public cloud. In order to execute higher flexibility and deployment options, the data and applications are free to move between the private and public clouds. In case there is a high volume demand, then the public cloud can be an option to go with else the user could make use of an on-premise infrastructure for carrying out critical business operations.
Benefits of Public Cloud
- By choosing a public cloud, the user saves a lot of money. This is because the user saves the complete IT expenditure by not installing, operating and maintaining the servers. He doesn’t need to spend a single money on the physical IT infrastructure.
- Public cloud offers a high level of scalability enabling the users to scale resources such as bandwidth, RAM and storage based on the business requirements. When not needed, these resources can be scaled.
- The public cloud comprises a large number of servers and networks that have redundant configurations. This means the cloud service continues to run along with other components even if a physical component fails to deliver or run.
- Various IaaS, PaaS and SaaS services present in the market on the public cloud model that can be readily used as a service by any Internet supporting device.
- Public clouds can be situated anywhere using an active Internet connection. It is thus ensured that these services are readily available to the user, irrespective of his location.
Comparison of Features
Following is the table that compares different types of clouds on the basis of features like- scalability, security, performance and hardware.
| Features/Cloud | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| Scalability | Computing resources are highly scalable in a public cloud | Limited scalability as there are pre-customized hardware for certain clients | Same as the public cloud, the hybrid cloud also offers high scalability opportunities |
| Security | The user data is safe on a public supported by an enterprise-class firewall and also protection from hardware failure | While designing the cloud architecture according to his needs, the user is well aware of where his data resides | Hybrid cloud has the same level of security offerings as the public cloud. Here, the user gets integration options for adding an additional security layer |
| Performance | Since the same hardware is being shared with other users, there are chances that the performance might go down in case another client that is hosted on the same server faces a traffic surge. The level of performance is highly fluctuating depending on the load present on the server | In a private cloud environment, it allows the users to apply optimization techniques that can enhance the user performance | Since the hybrid clouds are a mixture of public and private cloud platforms, it allows a smooth workflow to take place between the private and public cloud, giving the businesses higher flexibility and data deployment options |
| Hardware | Public clouds are built over a complete virtualized environment and are a cost-effective solution that comprises of secure VMs as well as SAN storage, scalable RAM and a flexible bandwidth | A private cloud is designed solely for a single organization and can offer advantages like- scalability and self-service similar to the public cloud. A private cloud can be the best option for businesses having unpredictable demands | A hybrid cloud comprises of on-premise hardware along with cloud resources such that there is not a single point of failure and it can be utilized by the businesses that have a variable workload |
Growth of Public Cloud
According to a report published by Gartner in November 2019, it states that the global public cloud services market is forecasted to grow at 17% in 2020. The report further states that the value of the global cloud market would be $266.4 billion in 2020 as compared to $227.8 billion in 2019. SaaS is going to be the largest market segment and is predicted to be valued at $116 billion by 2020. The key driver behind the growth of SaaS will be due to the scalability of subscription-based software. IaaS segment is predicted to reach $50 billion by 2020 depicting a growth of 24% YoY.
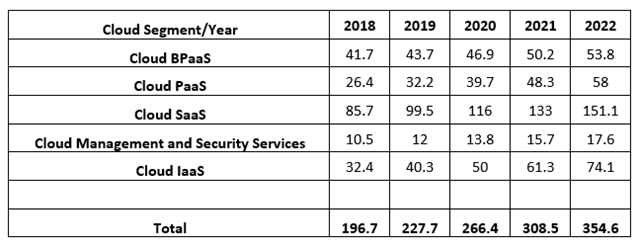
(All these values are in $ billion)
It has now become important for a business to understand their requirements when going for an optimum choice regarding the selection of the right cloud architecture. Different cloud platforms have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, however, the businesses need to consider the best out of them for their business. Public cloud offers its own set of advantages as it is mostly on a pay per consume basis, making it a flexible financial model. Public cloud isn’t inclusive of any infrastructure-related components, thereby making it easier for the businesses to scale their resources as per the demand. The inevitability of the public cloud can be considered due to all the stated advantages and its ever-rising growth on the global level.
