What is WAF?
A Web Application Firewall or WAF is a type of firewall that is used for monitoring, filtering or blocking the data packets as they move to and from across a website or web application. A WAF can be classified as- network-based, host or cloud-based and is often implemented using a reverse proxy that is placed in front of more than one website or web application. The WAF inspects every packet and works on a rule base for analyzing the Layer 7 web application logic and then filtering out the malicious traffic. Web application firewalls are a common security control mechanism being used by enterprises for protecting the web system against common exploits, malware infections along with hidden threats and vulnerabilities.
Types of WAF
Following are some of the common types of web application firewalls-
- Network-based WAFs: These WAFs are usually hardware-based and can minimize latency as they are installed locally, on-premise by the means of a dedicated appliance placed very closed to the application. A large number of network-based WAF vendors give the flexibility of duplicating the rules and settings along various appliances, thus making large-scale deployment, configuration, and management possible.
The biggest pitfall of using this type of WAF is the cost, as there is both an up-front capital expenditure as well as ongoing operational costs related to maintenance.
- Host-based WAFs: These WAFs can be fully integrated into the application code. The advantages of using a host-based WAF implementation include lowered costs and increased customization options. The host-based WAFs can be a challenge to manage as they require application libraries and depend on the local server resources for running efficiently. Thus to deploy host-based WAFs more staff inclusive of developers, system analysts along DevOps may be needed.
- Cloud-based WAFs: This kind of WAFs provide low-cost solutions to the businesses that need a turnkey product, thereby using the least number of resources for implementation and management. Cloud WAFs are easy to deploy and are readily present on a subscription basis and usually need a simple DNS or a proxy change for redirecting application traffic. There might be a challenge to place the responsibility to filter out the organization’s web application traffic using a third-party provider.
Working of WAF
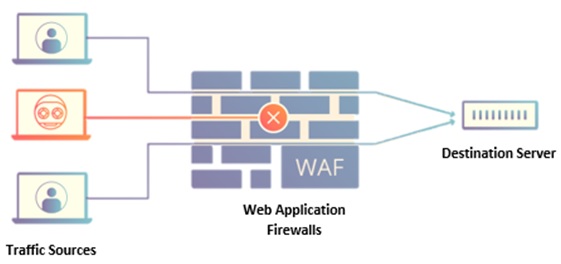
WAF is used for protecting web applications from any kind of attack like cross-site forgery, cross-site scripting, and SQL Injections to name a few. A WAF is a protocol layer 7 defense present in the OSI model and thus is not designed for providing defense against all kinds of attacks. This attack mitigation is generally encapsulated as a suite of tools that combined can create a holistic defense against a wide array of attack vectors. When the WAF is deployed against a web application, a barrier is formed between the web application and the Internet. A proxy server can protect the identity of a client machine with the help of an intermediary, however, a WAF is a type of reverse-proxy, thus protecting the server from exposure by allowing the clients to pass through the WAF before finally arriving at the server.
A WAF functions using a set of rules known as policies and these policies look to protect against vulnerabilities in the application by removing the malicious traffic. WAF is coupled with speed and ease along with policy modification that can be implemented for allowing faster responses to the diversified attacking vectors in case of a DDoS attack.
Benefits of Implementing WAF for Online Business
The primary working of WAF includes protection against sensitive data when exposed to a website. WAFs can be more helpful for those who have an online business like an e-commerce store or an online retailer.
These have strong reliability for storing private user data for enhancing the user experience on their sites. In case of weak cybersecurity measures in place, the businesses are open and vulnerable for hackers to infiltrate and gain access over the customer information. Once the website is under a major cyber attack, the company faces a heavy financial burden and can even lead to the dilution of trust among their prospective customers.
These customers look upon the businesses for securing their personal information. By deploying a strong WAF can be extremely powerful for protecting the incoming and outgoing traffic from a company’s website. This enables the WAF to automatically filter out the corrupt web traffic thus allowing the users to manually select the users they wish to block and deny them access to their websites. For any company, keeping the customer data private & secure is the top-notched priorities.
The WAFs can also be of great help to the ones that are unfamiliar with cybersecurity technicalities. Small and mid-sized businesses often find it difficult to account for the costs related to implementing cybersecurity solutions. For smaller companies dedicating time and resources could mean that they’re looking to hire a team of information security specialists who can monitor and maintain the complicated software. The primary aim of an SMB is usually growing their business and thus they place the issues pertaining to cybersecurity at the lowest. WAFs can be of great help for mitigating the issues that can be fatal or possess danger. In this case, WAFs act as an intermediary or an offsite security specialist that regularly monitors and analyzes the web traffic for preventing any loss of crucial information.
Positive and Negative WAF
Positive-Model WAF
A Positive Model WAF is responsible for allowing access to a specific set of characters by the means of predefined specific rules. Thus, whenever every rule that has been added provides greater access and when there are no rules in place, all the things are blocked by default. Using this model has the benefit of strictly limiting the vectors that an attacker can exploit as everything that is not allowed gets blocked automatically. The drawback of using this approach is that it tends to have a high level of care and input from the company that is implementing it for ensuring that legitimate customers are not shielded by any overaggressive rules. This confusion can usually be eradicated after carrying out “whitelisting”, i.e. creating rules for legal actions, whenever the services are implemented.
Negative-Model WAF
On the contrary, a Negative Model WAF works on the fact that most attackers use the uncovered exploits. When these exploits are blocked by the means of creating patches or updates for newer vulnerabilities that might occur, then the client needs to do very little and also ensuring that WAF remains up to date for security purposes. This model also reduces the stress of the users getting blocked as it is designed only for unlawful actions from occurring. One of the concerns with this model is that it is purely dependent on the team that looks after maintaining the WAF in order to stay updated on the exploits, thereby, allowing the attackers with much greater freedom for finding new vectors as any item that is not being blocked remains open for the users to try.
Market Growth of WAF
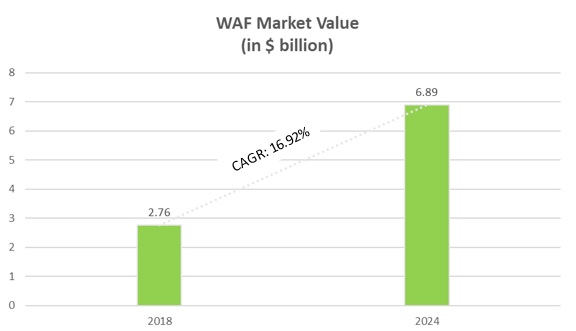
The market of WAF was valued at $2.76 billion in the year 2018 and is estimated to reach a value of $6.89 billion by the year 2024. During the forecasted period, i.e. 2019-2024, it is expected to grow with a CAGR of 16.92%. The current trend in this market lies with the ability to merge the abilities of network vulnerabilities scanners with the toolkits designed for web application security space. This has given the user the ability to use the data from one level and drive a more focused approach for another level.
- Web-based applications and services have changed how information delivery and exchange take place in various sectors today. The easy availability of information and richness of web services is placed along with a higher degree of trust.
- Some industry and government regulations need the deployment of a WAF solution for either implicit or explicit usage. The PCI-DSS is a well known and important regulation that can enable the adoption of WAF in the market. The WAF-related functionality can be implemented in software or hardware or run in an application device or even a typical server that runs on a common operating system.
- The main challenge that lies behind the implementation of WAF includes- cost and performance. Out of the two, performance remains the top-notched issue as the tools inspect the traffic incoming and outgoing at the application layer. Each protocol needs its own proxy applications thereby support for newer applications and protocols can be slow in emergence.
